You have been following a diet low in fermentable carbohydrates (FODMAPs) and your symptoms have improved, either totally or partially. It is now important to reintroduce fermentable carbohydrates back into your diet to determine which types and quantities give you symptoms. Reintroducing the fermentable carbohydrates that do not give you symptoms will increase the variety of foods and nutrients in your diet.
How are foods reintroduced?
One type of fermentable carbohydrate is reintroduced or ‘challenged’ at a time whilst remaining on a low FODMAP diet. This ensures the only difference in FODMAP intake comes from the challenge food.
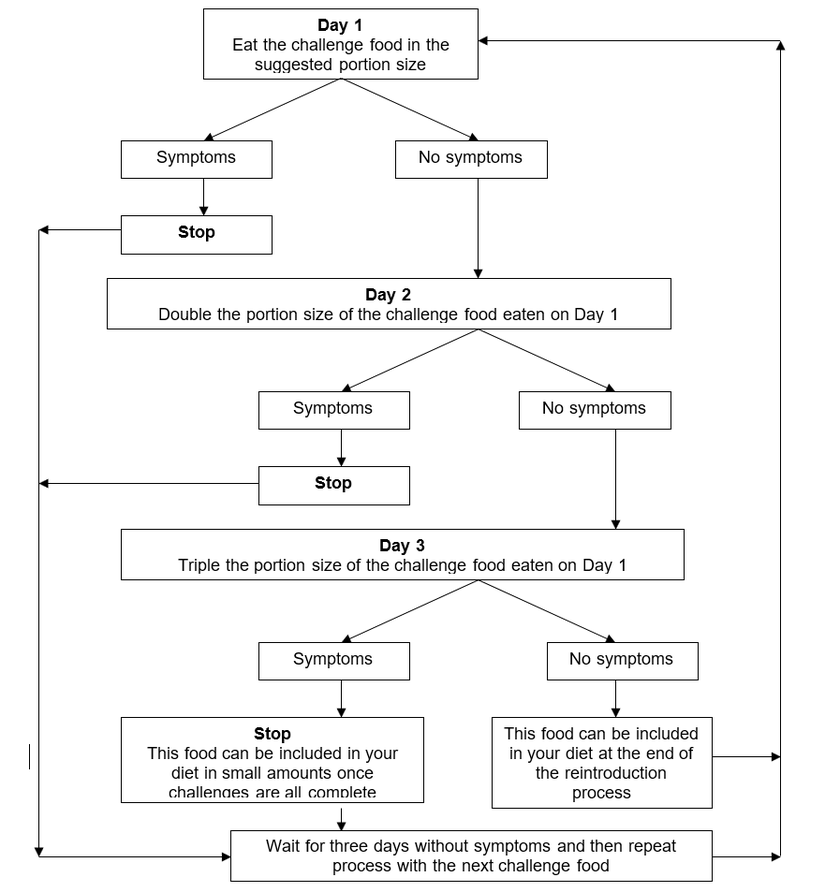
Each food should be challenged over 3 days in increasing portion sizes:
Day 1 - eat the challenge food in the portion size suggested
Day 2 – (if day 1 tolerated) double the portion of day 1
Day 3 - (if day 2 tolerated) triple the portion of day 1
The challenge process is summarised on the next page. The total reintroduction process will usually take up to 6-10 weeks.
No symptoms when challenging a food
If you do not experience symptoms when eating a challenge food on day 3 you can progress to the next food challenge. At the end of the reintroduction process you can include that food in your diet. It is important to remove the food you have just challenged before starting the next challenge to ensure your diet remains low FODMAP.
Symptoms when challenging a food
If you experience mild symptoms on eating a challenge food you can try the larger portion on the following day, however if you experience moderate-severe symptoms on eating a challenge food you should stop eating it. Do not challenge that food in a larger portion size. Wait until symptoms have settled (for most people this is 3 days) before challenging a different food; it is important that you are symptom free before moving onto the next food challenge.
If you experience symptoms on day 2 or day 3 of eating a challenge food but did not get symptoms on eating that food in a smaller portion size, you can include this food in your diet in the portion size that you tolerated at the end of the reintroduction process.
If you don't experience symptoms with a specific food containing a single FODMAP, then you are likely to tolerate other foods containing that specific FODMAP e.g. if you tolerate sweet potatoes, which contain mannitol, you are likely to tolerate cauliflower as well which also contains mannitol. The exception to this is fructans where individual foods need to be challenged.
Summary of the challenge process
What are the re-introductions?
- Fructose
- Lactose (if avoiding)
- Polyols (mannitol and sorbitol)
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Fructans
Fructose, Lactose, Polyols, GOS
Choose a challenge group and challenge one of the suggested foods in the suggested portion size. Use the same food for all 3 days of the challenge.
| Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Fructose
¼ mango Or 1 teaspoon honey |
Lactose
125mls cow’s milk Or 125g natural yoghurt |
Polyols
Sorbitol: ¼ avocado Or ½ corn on the cob Mannitol: 100g sweet potato Or 25g celery Or 60g cauliflower |
GOS
40g butter beans Or 80g chickpeas N.B. Do not use hummus, baked beans or other pulses for this challenge as they contain other high FODMAP ingredients |
Fructans
As people experience different symptoms with different fructan containing foods, you should challenge all of the following fructan containing foods, one at a time, starting with the portion sizes shown in the table below (day 1 portion sizes).
| Wheat (Bread) | Wheat (Pasta) | Wheat (Cereal) | Onion | Garlic | Leeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat (Bread) 1 slice wholemeal / white bread | Wheat (Pasta) 5 tablespoons cooked pasta |
Wheat (Cereal)
1 Weetabix Or 1 tablespoon Bran flakes |
Onion
1 tablespoon cooked onion (in a low FODMAP meal) |
Garlic
1/4 clove of raw or cooked garlic in a low FODMAP meal |
Leeks ½ leek (in low fermentable meal) |
If you can tolerate leeks you should be able to tolerate these high fructan foods: grapefruit, pomegranate, beetroot, brussels sprouts, savoy cabbage and okra.
Garlic and onion powder are concentrate forms of FODMAPs so are likely to cause symptoms if onion and garlic do. Small amounts may be tolerated when eaten with other foods.
NB: If the portions size on day 2 or day 3 is larger than you would usually eat, split it across different meals in the day.
Foods containing more than one type of FODMAP
Foods that contain more than 1 type of fermentable carbohydrate are challenged after the individual FODMAP foods have been trialled (see table 1 on last pages of booklet).
Fruit and vegetables containing more than one fermentable carbohydrate can be challenged in these portion sizes: day 1 - 40g; day 2 - 80g; day 3 - 120g
Long-term
Once you have completed the food challenges and have identified which foods trigger symptoms/in what quantities, you can begin to gradually reintroduce the foods that didn’t trigger symptoms back into your diet. You may find that having more than one high FODMAP food in a meal will increase the risk of symptoms so experiment with the amount you can tolerate. If you know a food gives you symptoms if you eat it everyday, but you want to include it in your diet, consider having it less frequently, for example every 3 days. If you do get symptoms, it is important to remember you are not causing yourself any damage.
Questions and answers
How should I record the reintroduction process?
It may help to keep a food and symptom diary during the reintroduction process to keep a list of those foods tolerated and at which quantities. For example:
| Day | Food and quantity | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Food and quantity 40g of butter beans | Symptoms None (tolerated) |
| Day 2 | Food and quantity 80g of butter beans |
Symptoms
Mild flatulence (tolerated <80g) |
| Day 3 | Food and quantity 120g of butter beans |
Symptoms
Abdominal discomfort, bloating |
What if I do not usually eat one of the challenge foods?
If you do not usually eat one of the suggested challenge foods, you do not have to reintroduce it. You may want to replace it with a different food that contains the same type of fermentable carbohydrate (see table 1 on last pages of the booklet).
What if I am unsure about my tolerance of a food that I have challenged?
If this is the case, wait for three days without symptoms and challenge this food again, this can be done at a later date if you want.
What if I am unsure about my tolerance of a food that is not on the ‘foods to avoid’ list?
If this is the case, you should challenge that food in the same way as for other challenge foods. These kind of foods may include other common trigger foods for IBS e.g. chilli spice, caffeine or alcohol.
What if I don’t get any symptoms at all during the challenge process?
If your symptoms improved during the restricted stage of the low FODMAP diet it is likely high FODMAP foods were triggering your symptoms. However, some people will find that during the reintroduction stage, when they challenge each individual challenge group no symptoms are triggered. This means no particular type of fermentable carbohydrate triggers symptoms on its own and it was likely the total amount of high FODMAP foods you were eating before that triggered symptoms.
Everyone has a threshold level of tolerance to fermentable carbohydrates and may only experience symptoms if a large amount is eaten over a short period of time or multiple different FODMAP containing foods are eaten at one meal.
Can I eat out during the challenge process?
It is best to avoid eating out during the challenge process to ensure your diet is low in fermentable carbohydrates.
Can I drink alcohol and caffeine?
You can drink alcohol and caffeine if you usually tolerate these but it is best to have a consistent amount throughout the challenge process.
What other factors may influence IBS symptoms?
Diet is unlikely to be the only cause of your IBS symptoms and your tolerance to FODMAP foods may fluctuate according to the other things going on in your life. For example if you are having a stressful period at work or at home you may find you are more sensitive to some FODMAP containing foods, equally on holiday you may find yourself less sensitive to FODMAP foods you would usually consider trigger foods.
Enzymes
There are oral enzymes available to purchase from pharmacies or on-line which can help digest certain FODMAPs. These enzymes may improve tolerance to some high FODMAP foods. Please follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how to use them.
Lactose foods: lactase enzymes can help digest lactose. These can be tablets or drops. Check ingredients for other FODMAP ingredients, e.g sorbitol or mannitol.
GOS foods: Alpha-galactosidase enzymes can help digest GOS foods. They can help reduce wind when eating large amounts of these FODMAP foods.
Who can I contact for advice?
Dietitian: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contact Number: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contact Email: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
| Food | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Sorbitol | Fructose Mannitol | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Cereals and flour | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Barley, Amaranth | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Freekeh, Lupin | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Coconut flour | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Spelt pasta | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Rye | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Wheat | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Dairy | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Cow’s milk | Fructose | Lactose ü | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Custard | Fructose | Lactose ü | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Cream cheese | Fructose | Lactose ü | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Ice cream (cow’s milk) | Fructose | Lactose ü | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Yoghurt (cow’s milk) | Fructose | Lactose ü | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Nuts | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Cashews, pistachios | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Almond, Hazelnut | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Plant-based protein foods | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Tofu Silken | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food TVP Soy Protein | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Sota Mince | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Fruit | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Apple | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Apricot (fresh) | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Apricot (dried) | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Banana (ripe) | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Blackberry | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Boysenberry | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Cherry | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Coconut | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Currants, raisins | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Dates | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Fig (fresh) | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Fig (dried) | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Goji berries | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Grapefruit | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Lychee | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Mango | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Nectarine | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Peach | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Pear | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Plum, prune | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Pomegranate | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Sharon Fruit | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Sultanas | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Watermelon | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans |
| Food | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Food | Fructose Fructose | Lactose Lactose | Polyols Polyols | GOS GOS | Fructans Fructans |
| Food Sorbitol | Fructose Mannitol | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Vegetables | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Artichoke (canned) | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Asparagus | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Avocado | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Beetroot | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Brussels sprouts | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Broccoli | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Butternut squash | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans ü |
| Food Cassava | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Cauliflower | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans |
| Food Celery | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans |
| Food Chicory root | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Fennel bulb | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans |
| Food Garlic | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Globe Artichoke | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Jerusalem artichoke | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Leek | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Mangetout | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans ü |
| Food Mushroom button | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans |
| Food Mushroom enoki, Portobello, shiitake | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans |
| Food Okra | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Onion | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Peas (frozen) | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Spring onion (white part) | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Sugar snap peas | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Savoy Cabbage | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Sweetcorn (fresh) | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Sweet potato | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS ü | Fructans |
| Food Beans and Pulses | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Adzuki Beans | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Baked beans | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Black eyed peas | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Broad beans | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Butter beans | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Chickpeas | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Lentils | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Red Kidney Beans | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Miscellaneous | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Honey | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Agave (light) | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Agave (dark) | Fructose ü | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Sugar free mints and chewing gum | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS ü | Fructans |
| Food Oligofructose, inulin, FOS | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Dandelion tea | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Camomile tea | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Fennel tea | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans ü |
| Food Food | Fructose Fructose | Lactose Lactose | Polyols Polyols | GOS GOS | Fructans Fructans |
| Food Sorbitol | Fructose Mannitol | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Oolong tea | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Chai tea | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols | GOS | Fructans |
| Food Coconut water | Fructose | Lactose | Polyols ü | GOS | Fructans |
We are smoke-free
Smoking is not allowed anywhere on the hospital campus. For advice and support in quitting, contact your GP or the free NHS stop smoking helpline on 0800 169 0 169.
Other formats
Help accessing this information in other formats is available. To find out more about the services we provide, please visit our patient information help page (see link below) or telephone 01223 256998. www.cuh.nhs.uk/contact-us/accessible-information/
Contact us
Cambridge University Hospitals
NHS Foundation Trust
Hills Road, Cambridge
CB2 0QQ
Telephone +44 (0)1223 245151
https://www.cuh.nhs.uk/contact-us/contact-enquiries/

