Thyroid cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the thyroid gland start to divide and grow in an uncontrolled way, forming a tumour.
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck, just below the voice box (larynx). The thyroid gland is part of the endocrine system, which makes and releases hormones that help control the way the body functions.
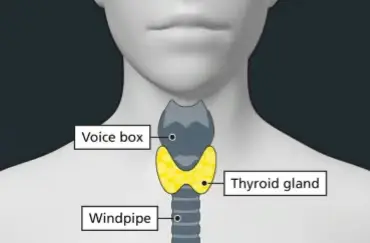
The most common symptom of thyroid cancer is a painless lump in the front, lower part of the neck. Most thyroid lumps are not cancerous (benign) however, it is important to get any lump checked.
Other common symptoms of thyroid cancer include:
- pain in the front of the neck
- difficulty swallowing
- changes in voice
- a sore throat
The most common types of thyroid cancer are papillary thyroid cancer (more common in younger people) and follicular thyroid cancer (mostly found in middle-aged people). These types of thyroid cancer together are called differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC).
Other less common types of thyroid cancer include:
- medullary thyroid cancer (MTC)
- anaplastic thyroid cancer
- thyroid lymphomas
Treatment for thyroid cancer at CUH
The treatment you have depends on several factors, which include:
- the type of the cancer
- the stage of the cancer
- if the cancer has spread
- your general health
A team of specialists at CUH will meet to discuss your condition and to make a recommendation about the best possible treatment for you.
You, along with your clinician, will then discuss your treatment recommendations at the clinic appointment and decide on the right treatment plan for you. Your clinician will explain different treatment options and possible side effects.
The treatment for thyroid cancer can include:
- surgery
- hormone therapy
- radioactive iodine treatment
- targeted therapy
- radiotherapy
- active surveillance
- chemotherapy (rarely)
Surgery is usually the main treatment for most types of thyroid cancer.
Depending on the type and stage of the cancer, surgery can remove all the thyroid (total thyroidectomy) of just a part of it (partial thyroidectomy or lobectomy). If the cancer has spread or is at high risk of spreading, your surgeon may also remove the lymph nodes in your neck.
At times however, you may require more than one treatment or a combination of different treatments to give the best chance of long-term cure and to help reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
If treatment is likely to have an effect on your speech or swallowing, your doctor and nurse will talk to you about this. Your clinical team will help you plan your treatment so the effect on those is as little as possible.
You may also see different specialists such as speech and language therapist (SLT), or dietitian, who will support you during your treatment.
Read more about the different types of treatment on our website.

