Penile cancer (cancer of the penis) is a rare cancer that starts when the abnormal cells begin to divide and grow in an uncontrolled way. It can develop anywhere on the penis but it mostly affects the skin of the penis and the foreskin, which covers the head of the penis.
The penis is the male reproductive organ responsible for urination and sexual intercourse. It contains a tube called the urethra, which carries semen (sperm) from the testicles and urine (pee) from the bladder out of the body.
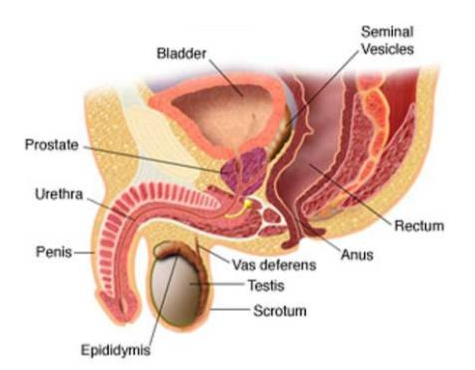
Signs and symptoms of penile cancer include:
- a growth, lump or sore (ulcer) anywhere on the penis
- thickening or raised areas anywhere on the penis
- changes in the colour of the skin or the foreskin, such as redness or white patches
- bleeding or foul-smelling discharge from the penis
- a lump, pain, bleeding or discharge from underneath the foreskin
The most common type of penile cancer is the squamous cell carcinoma, which originates in the outer layer of the skin (epithelium).
Rarer types of cancer that can affect the penis include:
- melanoma
- basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
- adenocarcinoma
- urothelial carcinoma
- sarcoma
Treatment for penile cancer
The treatment you have depends on several factors, which include:
- the type and size of the cancer
- the stage of the cancer
- your age
- your general health
Once the diagnosis of penile cancer is confirmed at CUH, patients are referred to Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (NNUH) for further review and management. NNUH is a specialist centre for the East of England.
You, along with your clinician at NNUH, will then discuss your treatment recommendations at the clinic appointment and decide on the right treatment plan for you. Your clinician will explain the different treatment options and possible side effects.
The treatment for penile cancer can include:
- surgery
- chemotherapy creams
- laser treatment
- cryotherapy
- chemotherapy
- radiotherapy
- clinical trials
At times, you may require more than one treatment or a combination of different treatments to give the best chance of long-term cure and to help reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
Read more about the different types of treatment on our website.

