Ovarian cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the ovary, fallopian tube or peritoneum begin to grow and divide in an uncontrolled way, eventually forming a growth (tumour).
The ovaries are 2 small, oval-shaped organs in the pelvis that store the eggs needed to make babies. They are on either side of the womb (uterus), close to the fallopian tubes. Fallopian tubes link the ovaries to the womb. A layer of tissue that supports the ovaries is called the peritoneum.
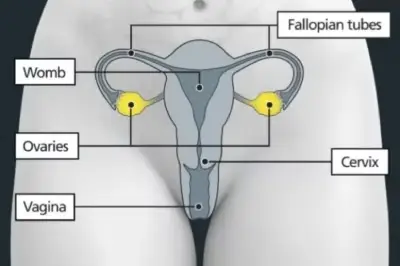
Cancers of the ovary, fallopian tube and of the peritoneum are very similar and therefore treated in the same way.
Common symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
- swollen or painful tummy
- feeling bloated
- pain in the back
- constipation or diarrhoea
- loss of appetite
- urinary changes
Most ovarian cancers start in the cells covering the ovaries and are called epithelial ovarian cancers. Epithelial ovarian cancers are then further categorised into several sub-types, based on the type and characteristics of the cells involved. The main sub-types include high-grade serous, low-grade serous, mucinous, endometrioid, and clear cell cancers.
Rarer types of ovarian cancer include:
- germ cell tumours
- stromal tumours
- sarcomas
Treatment for ovarian cancer at CUH
The treatment you have depends on several factors, which include:
- the type and size of the cancer
- the stage of the cancer
- your general health
- whether you want to get pregnant in future
A team of specialists at CUH will meet to discuss your condition and to make a recommendation about the best possible treatment for you.
You, along with your clinician, will then discuss your treatment recommendations at the clinic appointment and decide on the right treatment plan for you. Your clinician will explain the different treatments and their side effects.
The treatment for ovarian cancer can include:
- surgery
- chemotherapy
- targeted therapy
- hormone therapy
- radiotherapy
- clinical trials
At times, you may require more than one treatment or a combination of different treatments to give the best chance of long-term cure and to help reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
Read more about the different types of treatment on our website.

